A ribbon is a graphic user concept for application programs; it connects the menu control and toolbar elements.
Ribbon Structure
Application commands are shown as control elements. These control elements are grouped on a horizontal bar at the top edge of the application window. Groups which belong together are grouped into tabs. All tabs together and some special control elements make up the application's ribbon.
Figure: Ribbon with Start Tab
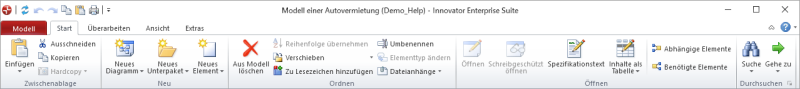
As with any other normal menu bar, terms which represent term groups can be found in the program window's header, e.g. Start, View or Design. Clicking on the term does not expand a menu; a tab containing the applicable commands appears instead. Each menu has its own tab.
Icons within the ribbon are grouped with similar icons, although this is automatically changed depending on resolution and/or screen size. The fact that more commands fit in the tabs means that you do not have to use dialogs (e.g. for paragraph formatting) as often.
Frequently-used commands can also be added to the toolbar for quick access; this then means that these commands can be quickly accessed to be run, regardless of which tab is currently shown in the ribbon.
A special tab that is separately colored can be found to the left. The Model tab primarily contains commands for working with models as a whole.
Fixed and Context-Sensitive Tabs
The ribbon always contains the Model tab and the Start, Review, View, Import/Export and Extras standard tabs which contain groups and commands.
Other tabs only appear once you are in a certain context, e.g. if a diagram is opened for editing. They contain additional commands which can only be executed in this context. Context tabs are highlighted.
