Activity Diagram
An activity diagram describes precisely one activity. This activity contains actions, control flows and object flows which show the formal, graphic description of the activity's flow in its entirety.
Icon
 The icon is of a diagram with an activity in it.
The icon is of a diagram with an activity in it.
Owner Hierarchy/Prerequisites
-
An activity diagram shows the contents of precisely one activity.
-
The activity diagram always shows the complete activity.
-
Each activity needs one behaviored classifier; the activity should describe its behavior.
Use
The activity diagram can be created in the Model Structure below a behaviored classifier.
Dependencies between actions and elements from other diagrams are shown in the whiteboard diagram.
Elements in the Activity Diagram
The following model elements can be shown as nodes and edges in activity diagrams:
 Actions
Actions
An action is the base unit of the behavior specification. Actions in an activity are continuous, non-atomic activities. They are the smallest executable element within an activity. An action can be refined with other activities.
Outgoing flows should only be triggered due to the completion of the internal action, and not due to explicit events. If there are several outgoing flows, these must be made dependent on conditions.
An action takes an array of inputs and converts them into an array of results; the input set, output set or both sets can be empty. The semantic defines the interpretation of input and output sets for an array of specialized actions:
| Icon | Element | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|

|
Execute instruction | An action; its semantic depends on the respective implementation. |

|
Call operation | An action which transfers a query from an operation call to the target object; it can then trigger the call of the linked behavior. |

|
Call behavior | A call action which directly calls a behavior instead of a behavior property; this would indirectly lead to this behavior being triggered. |
|
Accept event | An action which waits for an event which fulfills the condition given to occur. |
|
Send signal | An action which creates a signal instance from the input data and transfers it to the target object where a reaction can trigger e.g. firing of transitions in state machines or executing of an activity. |

|
Send object | An action which transfers an object to the target object where a reaction can trigger e.g. firing of transitions in state machines or executing of an activity. |

|
BroadcastSignal action | An action which sends a signal to all possible target objects in the system. |
|
AcceptCall action | An action which represents receiving a synchronous call query. |
|
Reply action | An action which contains a set of return values and a value which contains the result of a previous AcceptCall action, in turn. |

|
RaiseException action | An action which triggers an exception. |

|
ClearAssociation action | An action which destroys all instances of a relationship which a certain object participates in. |

|
TestIdentity action | An action which returns the "true" value if both input values are identical; otherwise this is the "false" value. |

|
ReadSelf action | An action which queries an activity's context object. |

|
ReadStructuralFeature action | An action which identifies a structural property's values. |

|
CreateObject action | An action which creates a new instance of a classification. |

|
DestroyObject action | An action which destroys the object at its input pin upon runtime. |

|
CreateLink action | An action which creates instances of associations or association classes. |

|
ReadLink action | An action which navigates using association ends to retrieve other objects. |

|
DestroyLink action | An action which deletes instances of associations or association classes. |

|
ClearStructuralFeature action | An action which deletes all existing values from a structure property. |

|
Unmarshall action | An action which breaks down an object of a certain type into individual parts so that their values correspond to one structure property of this object respectively. |

|
RemoveStructuralFeatureValue action | A writing action which removes values from a structure property. |

|
AddStructuralFeatureValue action | A writing action which adds to a structure property value or replaces previous values. |

|
ValueSpecification action | An action which evaluates an expression for a value specification. |
 Object Node
Object Node
An object node is a node in the activity diagram which shows that an instance of a certain classifier is available at a certain point in the activity flow, normally in a particular state. Object nodes can be used in many different ways regardless of whether object flows flow in or out of this node.
| Icon | Element | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Activity parameter |
|
|
Input pin |
The pin notation for object nodes illustrates the relationship between an action and an object node as and input or output parameter of the action. The direction of the edges at the object node sets whether this is an input or output pin. |
|
Output pin | |

|
Value pin | |

|
Action pin | |

|
Data store | |

|
Central buffer |
 Control structures
Control structures
Control nodes are used to coordinate object and control flows between other nodes, whereas structure nodes are used for grouping actions within an activity
| Icon | Element | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
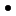
|
Initial node | The initial node starts an activity. It only has outflowing and no inflowing flows. Tokens are provided for all flows flowing out of the initial node when an activity is started. Unlike with states, activities can have one, none or multiple initial nodes. |
|
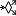
Decision node | A decision node has one inflowing and multiple outflowing flows; it is used to split the control flow into multiple alternatives which can be controlled by conditions. The decision node's token is consumed by the output node which fulfills the global conditions needed. |
|
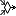
Merge node | The merge node rejoins various flows into one control flow. An action node after the merge node can consume a token if there is a token waiting at the merge node's input node. |
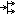
|
Fork node | A fork node splits the control flow into multiple parallel control flows. All outflowing flows are given a token so that all outflowing flows can start an independent subflow. |
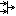
|
Join node | The join node rejoins parallel flows into one control flow. A token is only given to the next node in the flow once all inflowing flows have received tokens. |
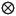
|
Flow final node | A final flow node ends one single parallel control flow within an activity. |
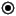
|
Activity final node | An end node completes an activity. It only has inflowing and no outflowing flows. As soon as a token reaches an end node, all other tokens are canceled and the activity is shown as completed. |
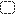
|
Structured activity node | On the one hand, a structured activity node can group an activity's elements to give it structure; on the other hand, it can be used as a special, executable node within control flows. |
|
Interruptible region | An interruptible region surrounds one or more actions and can be identified by an interruptible edge which starts within the interruptible region and has its target outside of this region. If the region is left using the interruptible edge, then all actions and/or flows being executed in the region are canceled; this is done by throwing all existing tokens. The flow continues at the interruptible edge's target node. |
 Edges
Edges
Edges in the activity diagram show the control and data flow between the diagram's nodes.
| Icon | Element | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|

|
Control flow edge |
The control flow within an activity is achieved with flows between the actions These flows can either directly lead to the next action or to a wait state, but can also be split and merged again with various connectors. A control flow is a directed edge which starts the activity node at the edge's target once the activity node is completed at the source. |
|
Object flow edge |
An object flow is a directed edge which transports data between object nodes. |
|
Exception handler | A special edge which transfers the exception to the activity node the exception is handled in. |
