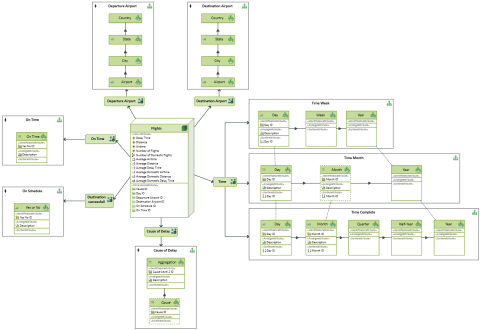
A cube diagram is a stereotype of the entity relationship diagram and can contain cubes and cube dimensions as nodes and their used hierarchies as container nodes.
You can use the established MID modeling tool to create Cube Diagrams.
Test the Innovator Enterprise Modeling Suite for free.
Definition
The cube diagram is a stereotype of the entity relationship diagram and can contain cubes and cube dimensions as nodes and their used hierarchies as container nodes.
 The icon shows a diagram of cubes and container nodes.
The icon shows a diagram of cubes and container nodes.
Use
Cube diagrams are used to model the analysis possibilities of multidimensional OLAP cubes to enable the coordination of specifications, for example, when communicating with specialist departments in the Business Intelligence area. The cubes and cube dimensions are displayed as nodes and the hierarchies they use are displayed as container nodes. The usage of hierarchies and the dimension precedence is displayed using edges.
Cube Diagram Elements
Nodes
The following model elements can be shown as nodes in cube diagrams:
| Icon | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|

|
Cube | A cube is a special form of a view of the entity relationship model. Linking a cube with a fact set using a from clause automatically only derives the local attributes as view attributes that represent the measures of the fact set. A cube can have any number of cube dimensions. |

|
Cube Dimension | A cube dimension connects the cube with a dimension and uses one or more dimension hierarchies in a complete model. |

|
Hierarchy | A hierarchy in a dimension forms a simple hierarchy; each level in the hierarchy can only have one sublevel. A complete and correct hierarchy contains one hierarchy level that represents the bottom-most dimension level in the dimension. The simple hierarchy is implemented as a list of hierarchy levels. In the list of a correct and complete hierarchy, the top-most level is the first element in the list, followed by a sublevel, then right through to the bottom-most level which is the last element in the list. |

|
Hierarchy Levels | A hierarchy level represents a dimension level and shows the content, redundant of its dimension attributes. You can edit a hierarchy level as a precedence of its dimension level in diagrams. This means that e.g. dimension attributes are actually created in the dimension level and shown in the hierarchy level. Dimension precedences that are shown between hierarchy levels actually run between their dimension levels. A link between a hierarchy and dimension entity or view is also stored at the dimension level. |

|
Display Attribute | There are three types of attributes in a dimension level: identification attributes, display attributes and sort attributes. These are linked with attributes from the Entity Relationship dimension set of their dimension level in a complete model. |

|
Identification Attribute | |

|
Sort Attribute |
Edges
Edges depict relationships between dimension levels in cube diagrams.
| Icon | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Cube Dimension Hierarchy Use | A cube dimension hierarchy use links a cube dimension with a hierarchy of its dimension. They are shown as edges in the cube diagram. |

|
Dimension Precedence | A dimension precedence is a hierarchy relationship between two dimension levels. It belongs to the sublevel and references the super level. |